In the competitive landscape of digital marketing, businesses are constantly searching for the most effective strategies to capture, nurture, and convert potential customers. Among these strategies, retargeting ads and remarketing campaigns stand out as powerful tools. Though often used interchangeably, they have distinct approaches and applications. This article delves into the nuances of retargeting ads and remarketing, helping you decide which strategy works best for your business.
Retargeting Ads vs Remarketing
Table of Contents
Understanding Retargeting Ads

Retargeting ads focus on re-engaging users who have already interacted with your website or mobile app but didn’t complete a desired action, such as making a purchase. These ads typically rely on browser cookies and target users as they browse other websites, ensuring your brand stays top of mind.
Retargeting works well for businesses aiming to:
- Boost conversion rates.
- Reinforce brand recall.
- Personalize customer experiences.
The process involves tracking user behavior on your site, segmenting audiences based on specific actions, and delivering tailored ads on platforms like Google Display Network, Facebook, or Instagram. For instance, if a user visits a product page but abandons their cart, retargeting ads can showcase that product alongside similar options.
Exploring Remarketing

Remarketing, often implemented through email campaigns, targets users who have already interacted with your business. Unlike retargeting, which leverages cookies, remarketing utilizes customer data, such as email addresses collected through opt-ins or previous transactions.
Remarketing excels in:
- Encouraging repeat purchases.
- Building long-term customer relationships.
- Promoting loyalty programs and exclusive offers.
For example, an e-commerce brand might send an email to past customers highlighting a limited-time sale on their favorite categories. Remarketing campaigns can also remind users of products they left in their cart, paired with discount codes or other incentives.
Key Differences Between Retargeting and Remarketing
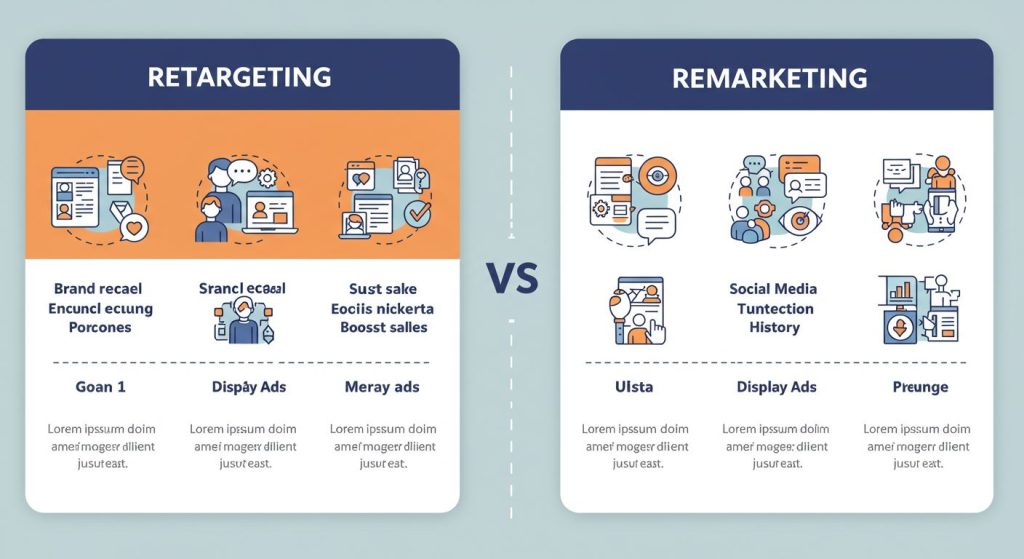
Though both strategies aim to re-engage users, they differ significantly in execution and purpose. Understanding these differences can help you align the right approach with your business goals.
Channel of Engagement
- Retargeting: Primarily occurs on ad networks, social media platforms, and third-party websites.
- Remarketing: Happens through direct communication channels like email.
Data Usage
- Retargeting: Uses cookie-based tracking to identify user behavior and preferences.
- Remarketing: Leverages first-party data, such as email addresses or purchase history.
Goal Orientation
- Retargeting: Focuses on converting website visitors into customers.
- Remarketing: Aims to deepen customer relationships and encourage repeat engagement.
When to Use Retargeting Ads

Retargeting ads are ideal when:
- Your website has high traffic but low conversion rates.
- You want to recover abandoned carts.
- You aim to increase brand visibility across multiple platforms.
For instance, businesses in e-commerce, SaaS, and travel often find retargeting invaluable for bringing users back into the sales funnel. By leveraging dynamic ads, you can tailor content to match the interests of specific audience segments.
When to Use Remarketing
Remarketing is effective when:
- You have a robust email list.
- You want to promote customer retention programs.
- Your goal is to upsell or cross-sell to existing customers.
For example, a SaaS company might use remarketing emails to upsell customers to a premium subscription. Similarly, a retail brand could promote exclusive discounts to loyalty program members.
Integrating Retargeting and Remarketing
For maximum impact, consider integrating retargeting and remarketing strategies. This hybrid approach ensures comprehensive coverage of your audience, addressing both first-time visitors and returning customers.
Example Integration Plan:
- Step 1: Use retargeting ads to re-engage users who abandon their carts.
- Step 2: Follow up with a remarketing email offering an exclusive discount.
- Step 3: Encourage loyalty by sending periodic emails featuring rewards or benefits for frequent purchases.
This combined strategy not only improves conversion rates but also fosters long-term customer relationships.
Measuring Success: KPIs for Retargeting and Remarketing
To evaluate the effectiveness of retargeting and remarketing, focus on key performance indicators (KPIs) such as:
- Click-through Rate (CTR): Measures the effectiveness of your ads.
- Conversion Rate: Indicates how many users complete the desired action.
- Return on Ad Spend (ROAS): Evaluates the profitability of retargeting campaigns.
- Email Open Rate: Reflects the engagement level of remarketing emails.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV): Gauges the long-term impact of remarketing.
Analyzing these metrics will help you optimize campaigns for better results.
Conclusion: Which Strategy is Best for Your Business?
The choice between retargeting ads and remarketing depends on your business goals, target audience, and available resources. While retargeting excels in converting first-time visitors, remarketing nurtures existing customers and builds loyalty. For many businesses, combining these strategies provides the best of both worlds.
To maximize success, ensure your campaigns are tailored to user behavior, consistently monitored, and aligned with broader marketing objectives. By doing so, you’ll not only drive conversions but also foster enduring customer relationships.